THE IMPORTANCE OF TIME MANAGEMENT
| Site: | e-Learning COMMON DIGITAL EDUCATIONAL PLATFORM for SOFT SKILLS & CULTURE OF LABOUR MARKET - DEPS-Skills |
| Course: | TIME MANAGEMENT (EN) |
| Book: | THE IMPORTANCE OF TIME MANAGEMENT |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Sunday, 14 September 2025, 11:17 PM |
1. Time Management
Time management is the process by which individuals or organizations plan and control how they spend their time to increase efficiency and productivity. It involves various strategies, methods, and tools that help people allocate their time optimally among different activities and tasks.
Time management is an essential skill that can help complete tasks more effectively and successfully, achieve personal and professional goals, and improve overall quality of life.
1.1. Why is Time Management Important?
-
Increases Efficiency and Productivity. By planning our time properly, we can complete more tasks in less time.
-
Reduces Stress. Knowing what needs to be done and when reduces anxiety and stress, as we have a clear action plan.
-
Improves Quality of Life. Effective time management allows us to dedicate more time to rest, hobbies, and spending time with loved ones.
-
Encourages Personal Growth. Time management helps us find time to learn new things, attend training, or read books, contributing to both personal and professional development.
-
Enhances Decision-Making. Having a clear plan and structure makes it easier to make decisions and set priorities.
1.2. Key Time Management Strategies
The time management process consists of several stages necessary for effectively managing work time. It includes planning, delegation, and monitoring as key components. Time analysis is also a fundamental stage in time management, helping to assess how time is spent and optimize productivity.
An important aspect of the time management process is rest time management, ensuring a balance between work and relaxation. The process can be divided into the following main components (see figure).
Fig. Time Management Process
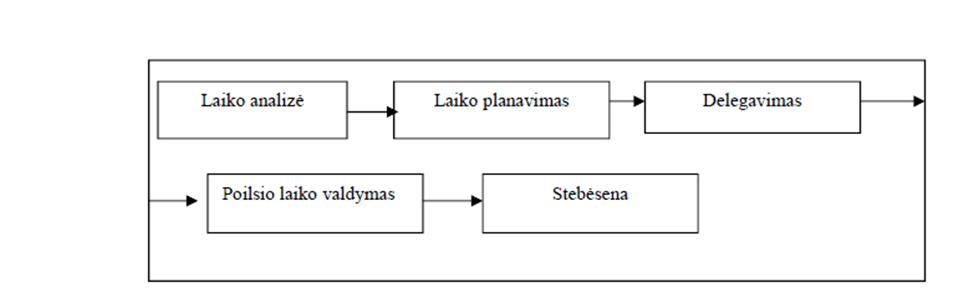
Source: Onodugo (2014), Ocak, Boyraz (2016), Piskorz et al. (2019)
1.3. Aspects of Time Management
Time Management Stages in the Time Management Process
Time management consists of several key stages that help individuals and organizations optimize their use of time. These stages include:
- Time Analysis – Examining how time is used and identifying time-consuming activities.
- Planning – Setting goals, determining priorities, and creating schedules and task lists.
- Delegation – Assigning tasks to competent individuals to distribute the workload efficiently.
- Rest Time Management – Incorporating breaks, rest periods, and strategies to avoid burnout.
- Monitoring – Tracking work duration, evaluating time usage, and making necessary adjustments.
Time Analysis
Time analysis is an essential and ongoing part of time management. It involves:
- Calculating the duration of each task.
- Identifying potential distractions and obstacles.
- Choosing the most suitable hours and days for different types of tasks.
- Recognizing time loss sources and finding ways to eliminate them.
- Establishing criteria for evaluating the importance of different tasks.
By analyzing how time is spent, individuals can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that important tasks receive more attention while minimizing time wasted on low-value activities. If a completed task does not yield the desired result, it may be necessary to eliminate or restructure it.
Time Evaluation
Time evaluation helps in:
- Establishing general principles for work organization and time-saving.
- Identifying challenges and finding the best solutions.
- Comparing planned vs. actual time spent on tasks.
- Enhancing time management skills through self-observation.
To improve time management skills, tracking and evaluating time usage is crucial. Each week, a specific amount of time should be allocated for planned tasks, and a comparison should be made between expected and actual time spent.
By the end of the week, individuals can review their time records and adjust their schedules accordingly. Weekly reviews help understand how much time is spent on tasks of varying complexity and improve long-term planning efficiency.
1.4. Tips for Effective Time Management
1.5. Time Planning
Time Planning
Time planning involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps while considering personal capabilities. The main function of time planning is the ability to organize tasks efficiently.
Core Principles of Time Planning
-
Goal Setting – The essence of planning lies in defining objectives and tasks. Clear goal-setting helps prioritize activities and determine which tasks are the most urgent and should be completed immediately. Well-defined goals provide direction, clarity, and an understanding of progress.
-
Time Estimation – To use time effectively, it is essential to estimate how long each task will take before starting.
-
Defining Objectives and Expected Outcomes – Setting specific goals and desired results helps maintain focus and motivation.
-
Prioritization – Identify which tasks are most important and eliminate unnecessary activities to stay focused on key responsibilities. Tasks should be organized by priority and assigned a specific timeframe for completion.
-
Task Management – Properly distributing tasks and understanding the actions required before completing larger projects ensures a structured and efficient workflow.
By applying effective time planning techniques, individuals can optimize their schedules, stay focused on essential tasks, and achieve their goals efficiently.
1.6. Short-Term Planning
It has been established that short-term planning has a greater impact on work performance than long-term planning. When planning for a shorter period, it is easier to adapt to changes and remain flexible. Therefore, it is recommended not only to plan work weekly but also to outline a daily work schedule. Large-scale projects can be assigned several days or divided into smaller tasks.
Task Delegation
Delegation or redistribution of authority refers to transferring tasks from one person to another. However, it is essential to evaluate which tasks can be delegated to others and which should be completed individually. Tasks should only be delegated to someone qualified to perform them.
Downward delegation occurs when a manager assigns tasks to subordinates. If a manager wants to delegate a task to an employee who lacks the necessary skills, they must allocate time for explanation and supervision. If an employee is given a task beyond their competence, they have the right to ask for guidance or clarification from the manager.
Principles for Effective Delegation
To delegate tasks efficiently, it is important to consider:
- Responsibility – The ability to take accountability for delegated tasks.
- Effective Communication – Clear and structured communication ensures proper task execution.
- Understanding the Scope of Responsibility – Leaders must define the level of responsibility for each employee.
Although management rules may seem strict, they are necessary for ensuring efficiency in the workplace. If employees do not fully understand workplace policies, they may face difficulties in completing tasks correctly.
1.7. Delegation Procedure
The delegation process strengthens employees' trust in their team, encourages them to think critically, and seek compromises. Employees begin to communicate more, share knowledge, and collaborate more effectively. A non-conflict work environment fosters creativity, innovation, and mutual trust among both internal and external stakeholders.
Managing Breaks and Rest Time
Rest time management is one of the key stages of time management. It is important to recognize when you are tired and when you need a break. Keeping time logs can help track when you work most productively, when fatigue sets in, and how long breaks should be. Some people work most efficiently in the morning, others perform better during the day, while some prefer to work at night.
Monitoring in Time Management
Monitoring ensures that everything is being carried out according to established plans, issued instructions, and defined principles. The purpose of monitoring is to identify weaknesses, correct mistakes, and prevent their recurrence.
Monitoring can be simple, such as analyzing reports, or complex, involving checking all processes.
Key Principles of Monitoring:
- Integration with all elements of the management process.
- Timeliness – ensuring that monitoring occurs at the right time.
- Comprehensiveness – covering all aspects of time management.
- Trust and Responsibility – establishing accountability within the team.
- Flexibility – allowing adjustments when needed.
- Utilization of Digital Control Methods – leveraging software and digital tracking tools for efficiency.
The Time Management Process
Time management is not limited to prioritizing tasks, planning, organizing, and delegating functions. It also includes time analysis and monitoring, which help improve time management skills.
During time evaluation, it is crucial to:
- Determine the duration and deadline for each task.
- Eliminate unnecessary tasks to avoid wasted time.
- Distribute tasks based on urgency and importance by creating structured schedules.
- Set criteria for delegation and assign responsible individuals for specific tasks.
- Analyze work-life balance to prevent burnout and improve efficiency.
- Conduct ongoing monitoring to ensure that all tasks are completed before deadlines.
By following these principles, individuals and organizations can optimize their time, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance overall productivity.
1.8. Practical Task
Watch the video and assess whether you apply similar time management practices.
Then, answer the test questions to evaluate how effectively you manage your time.
1.9. Key Time Management Strategies
Key Time Management Strategies
-
Goal Setting – Start by defining long-term and short-term goals. This helps clarify what you aim to achieve and focus on the most important tasks.
-
Prioritization – Use methods like the Eisenhower Matrix, which categorizes tasks into four groups:
- Urgent and Important
- Not Urgent but Important
- Urgent but Not Important
- Neither Urgent nor Important
-
Work Planning – Create daily, weekly, or monthly schedules that include all necessary tasks and activities. Use calendars, notebooks, or digital planning tools to stay organized.
-
Time Blocking – Allocate specific time blocks for tasks, avoiding unnecessary interruptions. This improves focus and efficiency.
-
Delegation – You don't have to do everything yourself. Delegate tasks when possible to focus on more critical work.
-
Rest and Breaks – Avoid overloading yourself. Regular breaks and proper rest are essential for maintaining high productivity levels.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve efficiency, reduce stress, and achieve better work-life balance.
