CRITICAL THINKING (EN)
-
3. IS WHAT YOU SEE THE TRUTH
-
Deepfake and AI.
In recent years, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technology have given rise to a phenomenon known as deepfake. The name comes from combining deep learning and fake. Deepfake technology enables the manipulation of video and audio content in a way that appears highly realistic. For instance, it can make someone on video seem to say something they never said or even place one person’s face onto someone else’s body.
While this technology can be used for creative purposes (e.g., in movies or advertising), it also poses significant risks, such as spreading misinformation, manipulating public opinion, or violating privacy. This makes the ability to recognize deepfakes increasingly important in today’s world.
Why should you learn to recognize deepfake?
- Misinformation. Deepfakes can be used to create fake news or manipulate recordings in ways that mislead viewers.
- Personal security. This technology is sometimes used to produce harmful content, such as fake compromising videos.
- Creative applications. On the positive side, deepfake offers intriguing possibilities in the entertainment industry, like recreating deceased actors for films.
Exercise:
Try to find the loopholes—where can you spot that a picture or video is fake?
How to spot AI-Generated Images?
- Unusual or Inconsistent Details: AI-generated images often contain minor, noticeable detail errors. Look for abnormalities like asymmetrical facial features, odd finger placement, or objects with strange proportions.
- Texture and Pattern Repetition: AI sometimes struggles with complex textures or patterns, leading to noticeable repetition or awkward transitions. Look for unnatural patterns in textures like hair, skin, clothing, or background elements.
- Lighting and Shadows: AI-generated images can have inconsistent or unrealistic lighting and shadows. Check if the lighting on different objects in the image matches and if the shadows are consistent with the light sources.
- Background Anomalies: Backgrounds in AI images can be a giveaway. Many are overly simplistic, overly complex, or contain elements that don’t belong. Pay attention to the background as much as the main subject.
- Facial Features: Faces generated by AI can sometimes appear slightly off. This can include oddities in the eyes (like reflections or iris shape), ears, or hair. These features are often subtly surreal or unnaturally symmetrical/asymmetrical.
- Contextual Errors: AI can struggle with context. An object might be out of place for the setting, or there might be a mismatch in the scale of objects. Consider whether everything in the image makes sense contextually.
- Text and Labels: AI often struggles with replicating coherent and contextually accurate text. If there’s text on the image, it can sometimes be jumbled, misspelled, or nonsensical in AI-generated images.
- Digital Artifacts: Look for signs of digital manipulation, like pixelation, strange colour patterns, or blur in areas where it doesn’t logically belong.
- Emotional Inconsistency: AI-generated faces may have expressions that don’t quite match the emotion or mood the image conveys.
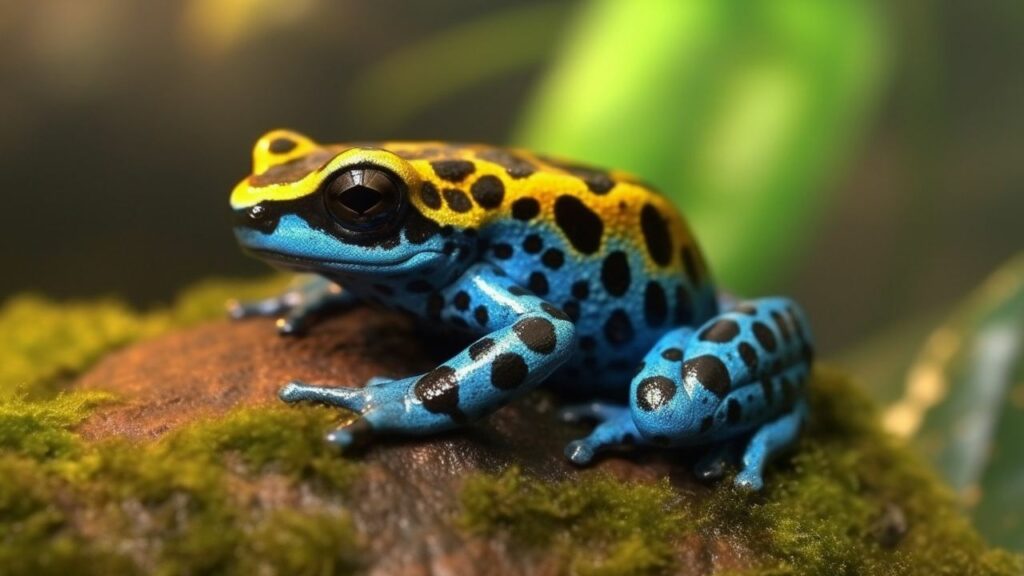
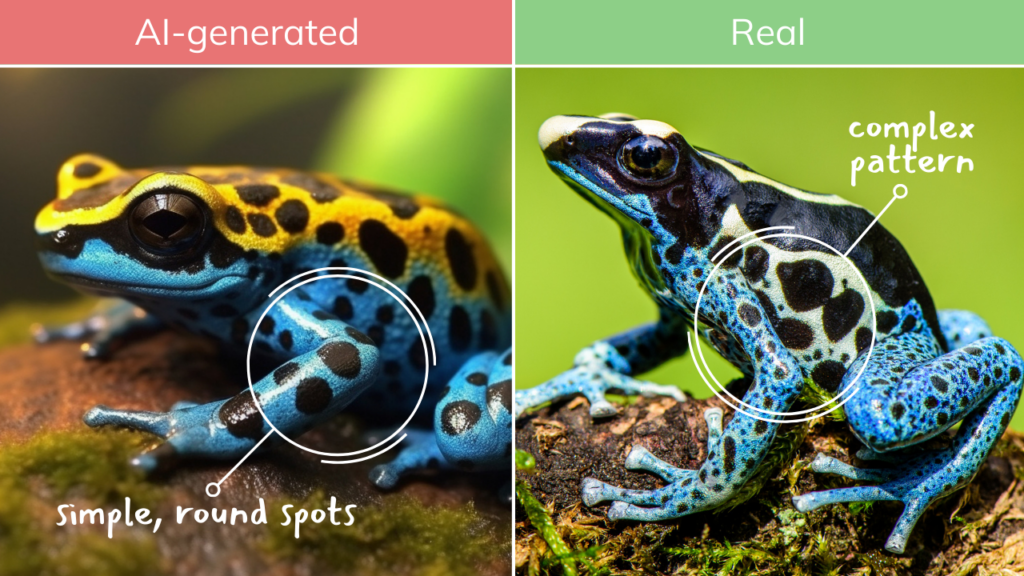
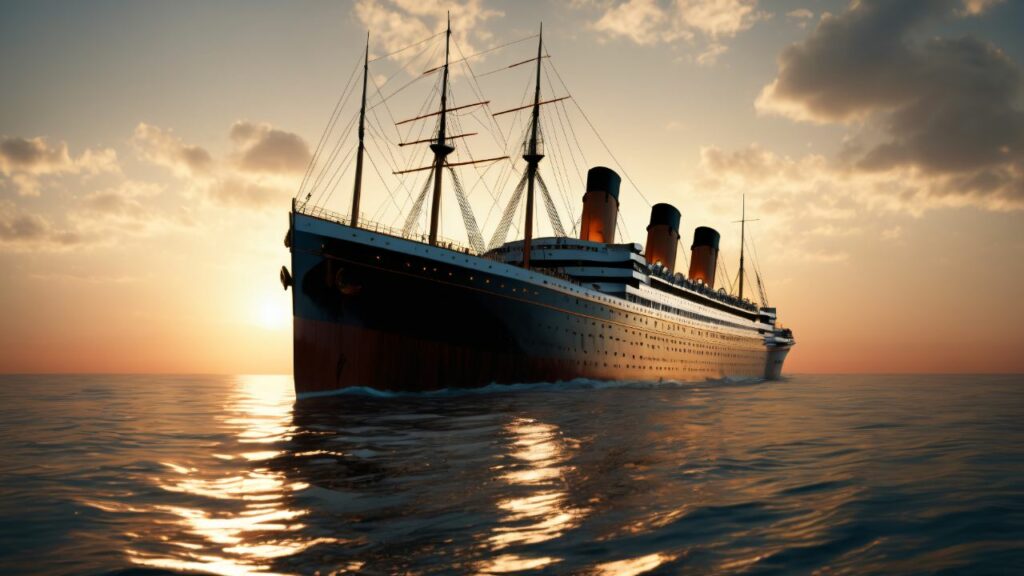
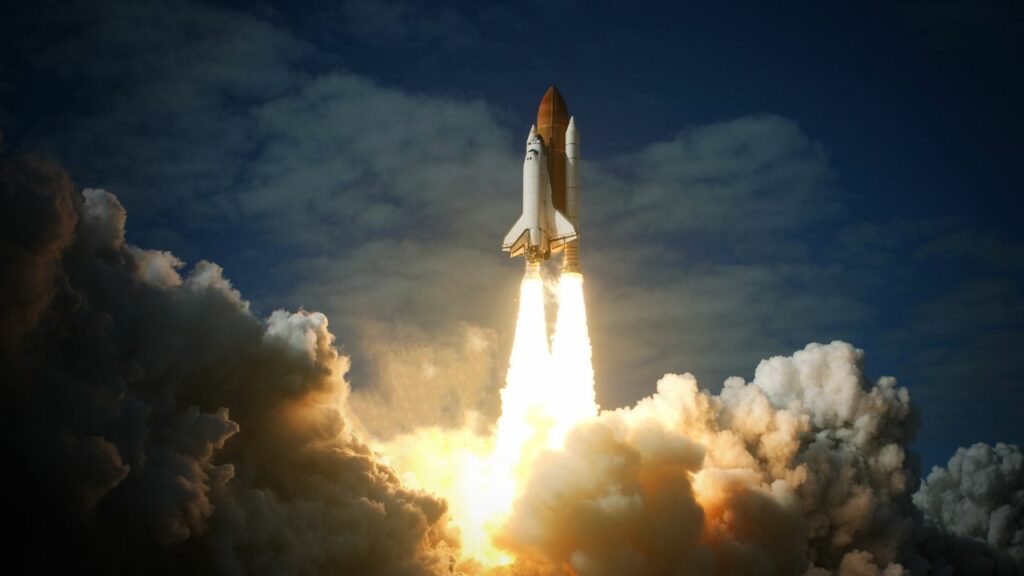
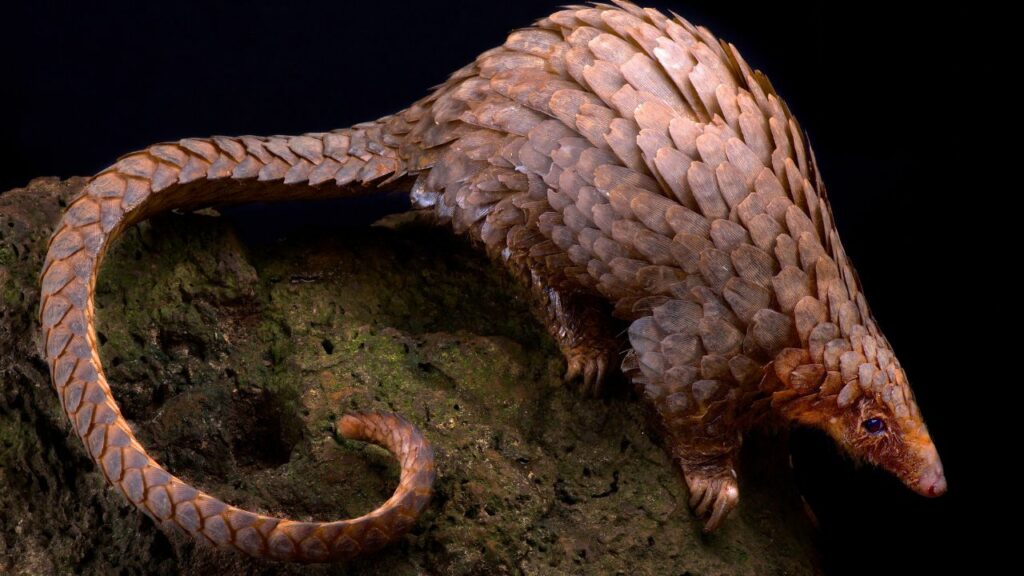











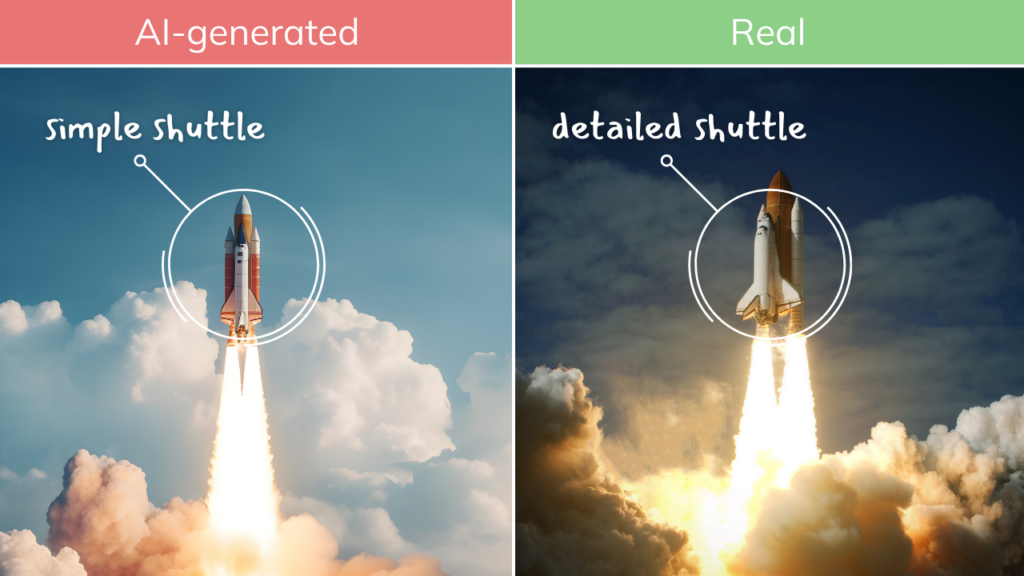





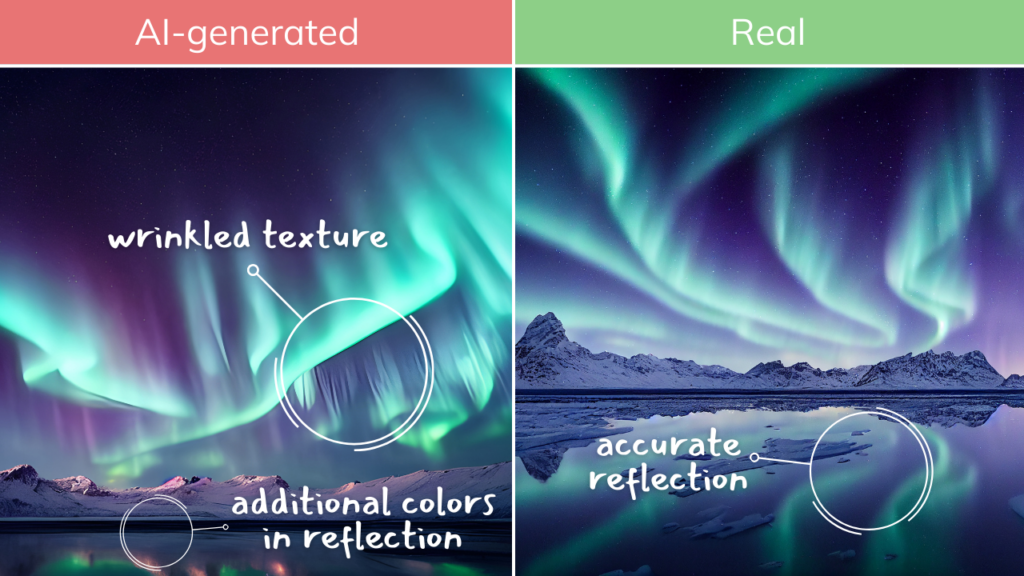


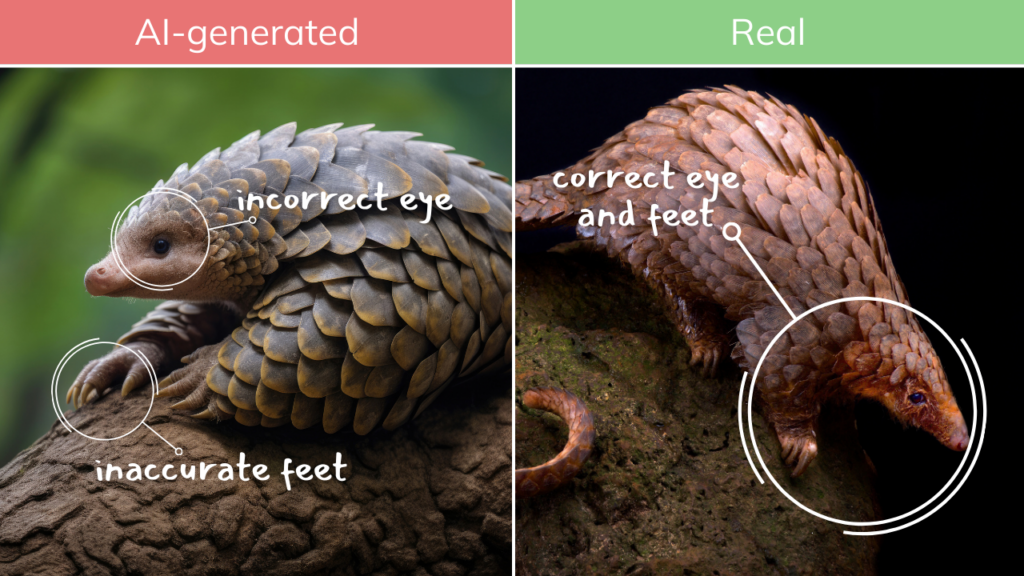



Exercise:
Try to find the loopholes—where can you spot that a picture or video is fake?
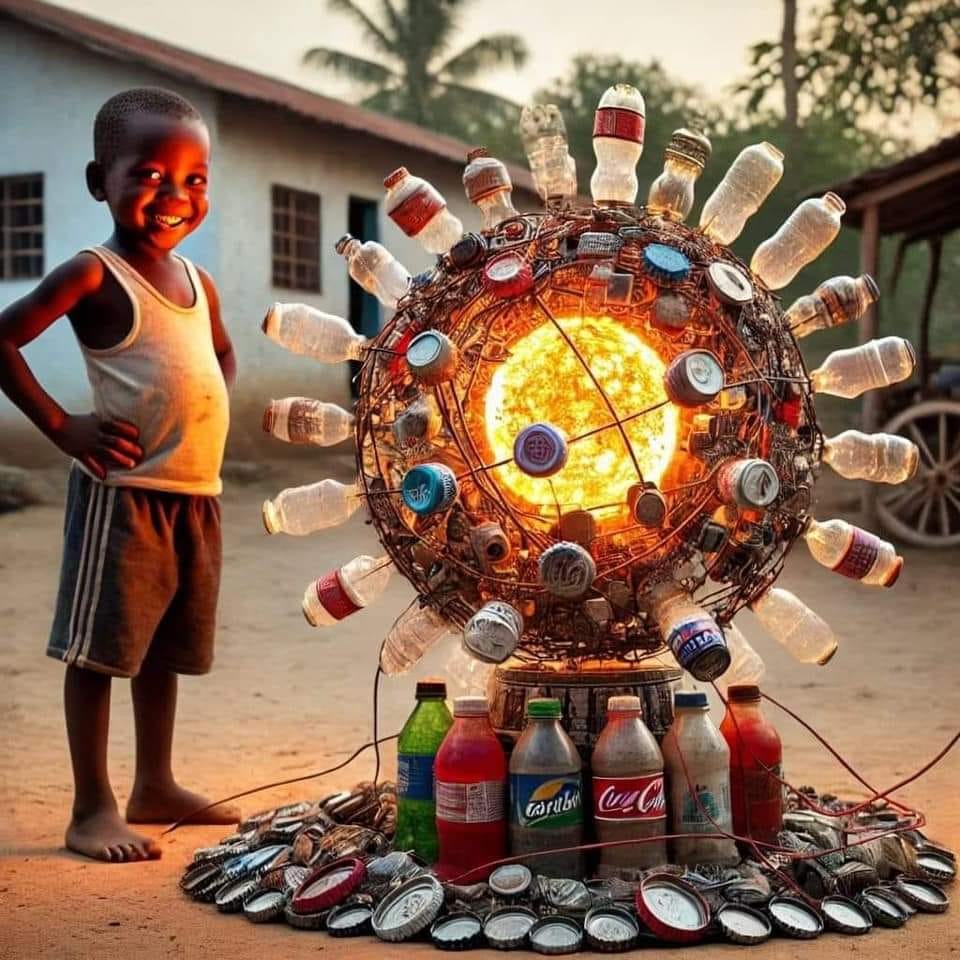
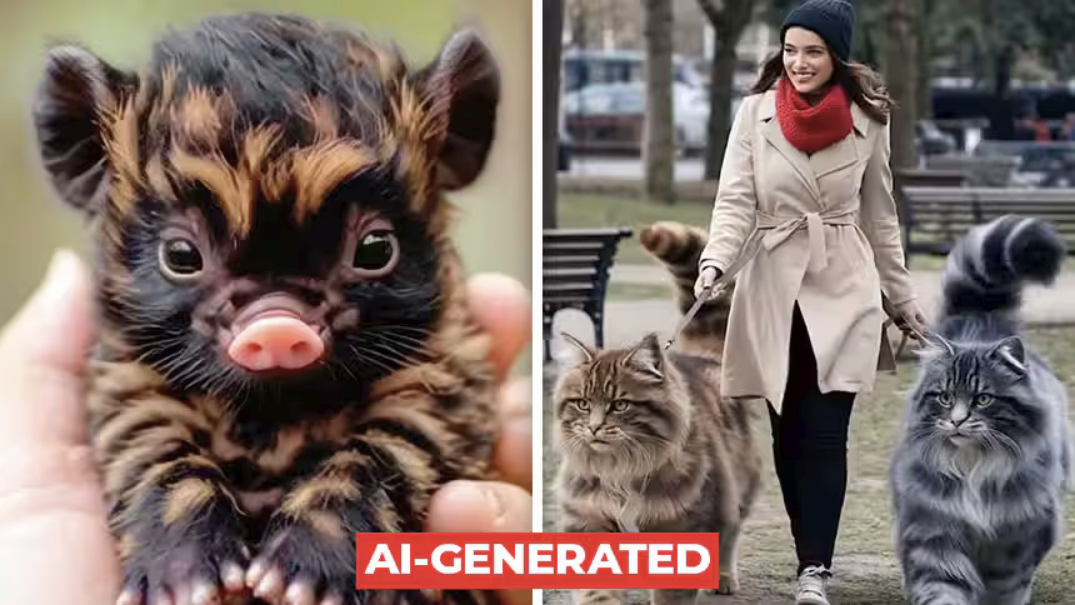
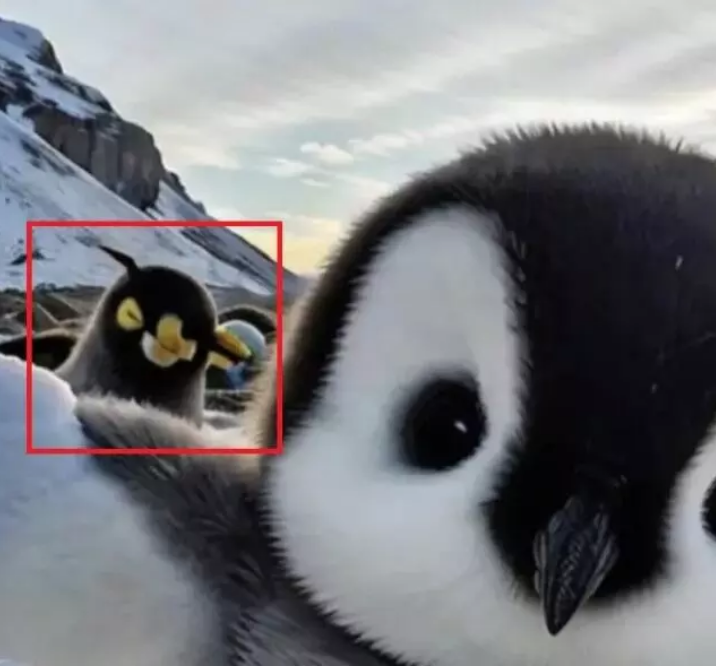







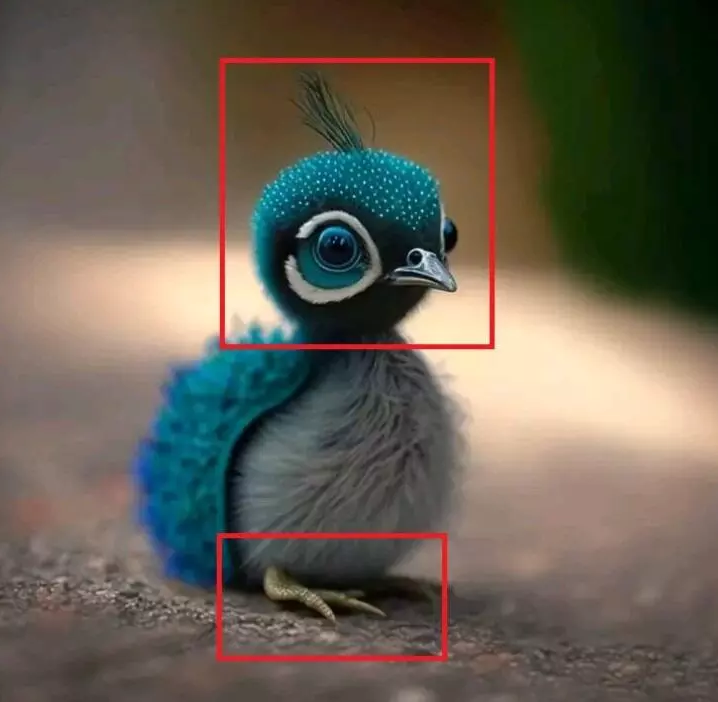
-

